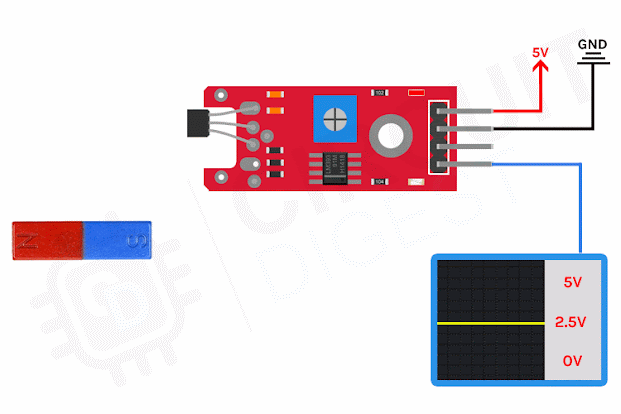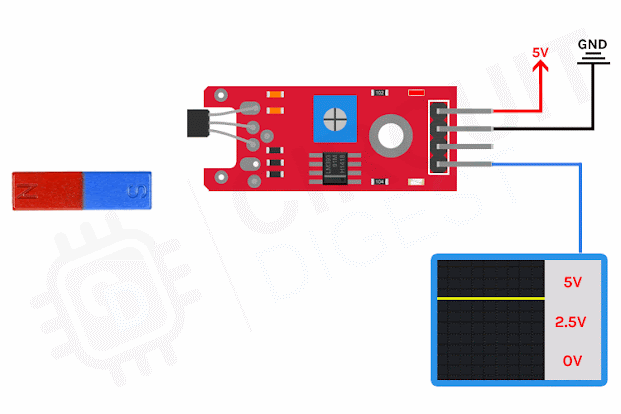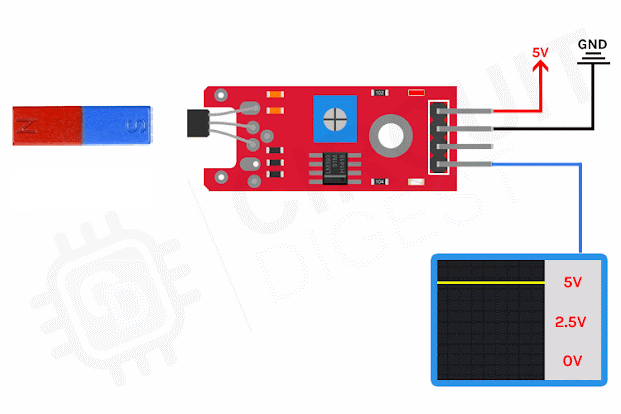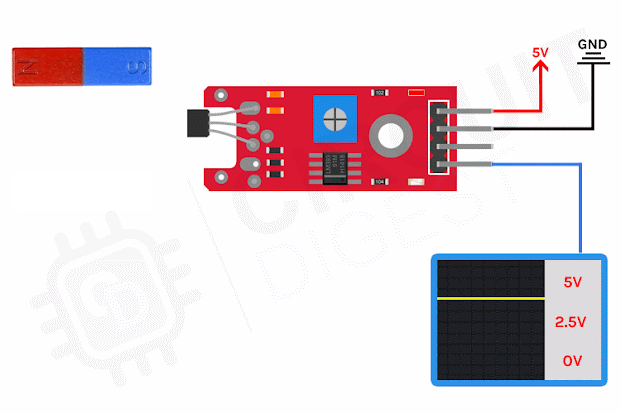
What is thermocouples and how it works?

A thermocouple is a device that is used to measure temperature. It is made up of two different metal wires, joined together to form a junction. When this junction gets hot or cold, a small amount of voltage is generated in between two junctions of two transistors, depending upon the material and the amount of voltage and we can measure the temperature very accurately. In theory, a thermocouple can be made up of any two different materials, but to improve linearity, accuracy, and temperature response specific materials are used to make the thermocouples. For example, the thermocouple made up of copper/constantan is known as the Type T thermocouple, the thermocouples made up of iron/constantan is known as the Type J thermocouple, and then finally the most popular K Type thermocouple is made up of combining alumel and chromel. When more than one thermocouples constructed from the same materials are combined they are called a thermopile. Constantan is a proprietary name for a copper-n...